Occupational therapy hand exercises are tailored to enhance hand function, strength, and dexterity, aiding individuals in regaining independence in daily activities through structured routines and tools like therapy putty.
Understanding Occupational Therapy
Occupational therapy (OT) is a rehabilitation approach focused on helping individuals perform daily activities despite physical, cognitive, or emotional challenges. It aims to enhance functional abilities and improve quality of life. OT addresses hand function, dexterity, and strength through tailored exercises and tools like therapy putty. Occupational therapists design personalized routines to address specific needs, such as regaining independence in tasks like writing or gripping objects. Hand exercises are a cornerstone of OT, particularly for conditions like arthritis or injuries, to restore mobility and reduce stiffness. By incorporating activities like coin picking or tendon gliding, OT helps individuals achieve practical goals and maintain independence. Resources such as downloadable PDF guides provide structured plans for home or clinical use, ensuring consistent progress in hand rehabilitation.
The Importance of Hand Exercises in Occupational Therapy
Hand exercises are a cornerstone of occupational therapy, playing a vital role in improving hand function, dexterity, and strength. These exercises are designed to address challenges such as limited mobility, stiffness, or pain, often resulting from conditions like arthritis or injuries. By enhancing range of motion and reducing stiffness, hand exercises help individuals perform daily activities with greater ease. They are particularly beneficial for improving grip strength and coordination, which are essential for tasks like writing, cooking, or using tools. Regular hand exercises also support rehabilitation, enabling individuals to regain independence in their daily lives. Occupational therapists often recommend structured routines, including activities like coin picking or tendon gliding, to target specific hand functions and promote overall hand health.

Types of Hand Exercises in Occupational Therapy
Hand exercises in occupational therapy include therapy putty, coin and small object exercises, passive and active motion, tendon gliding, opposition, and pronation/supination exercises to improve strength and mobility.
Therapy Putty Exercises
Therapy putty exercises are a popular tool in occupational therapy to improve hand strength, dexterity, and coordination. These exercises involve manipulating therapy putty, a pliable material, through various grips and movements. Common exercises include the power grip, where the putty is squeezed flat with the entire hand, and the flat pinch, where the putty is pinched between the fingers. Another exercise is the full grip, where the putty is shaped into a log and held vertically within the hand. Therapy putty is color-coded by resistance level, allowing individuals to progress as their strength improves. These exercises are effective for enhancing finger coordination, reducing stiffness, and rebuilding hand function. They are often used for rehabilitation after injuries or surgeries and are adaptable to different skill levels, making them a versatile and effective component of hand therapy routines.
Coin and Small Object Exercises
Coin and small object exercises are effective for improving hand dexterity, coordination, and fine motor skills. These exercises involve picking up and manipulating small items like coins, buttons, or beads. One common activity is to spread coins on a table and pick them up one by one, placing them into a container. This task enhances grip strength and finger control. Another exercise involves holding a small object, such as a coin, in the palm and flipping it over using the fingers. These exercises are particularly beneficial for individuals with conditions like arthritis, as they improve flexibility and range of motion. Using various small objects, such as pins or toothpicks, adds variety and challenges hand function further. Regular practice of these exercises can significantly enhance daily hand function and independence.
Passive and Active Motion Exercises
Passive and active motion exercises are essential for improving hand mobility and reducing stiffness. Passive exercises involve using the uninjured hand to gently move the injured hand through a range of motions, such as wrist flexion, extension, and rotation. These exercises help maintain joint mobility without requiring effort from the injured hand. Active exercises, on the other hand, require the individual to move their hand and fingers independently, such as bending fingers toward the palm or spreading them wide. Both types of exercises are beneficial for conditions like arthritis, as they enhance flexibility and reduce discomfort. It’s important to perform these exercises slowly and within a pain-free range to avoid swelling. Regular practice can significantly improve hand function and overall dexterity, making daily activities easier to perform.
Tendon Gliding Exercises
Tendon gliding exercises are designed to improve the smooth movement of tendons in the hands, enhancing flexibility and reducing stiffness. These exercises involve specific finger movements that simulate the natural gliding of tendons within the hand. For example, making an “O” shape by touching the thumb to each fingertip, one at a time, helps promote tendon mobility. Another exercise involves bending the fingers down toward the palm and then straightening them, ensuring tendons glide freely. Regular practice of these exercises can prevent tendon adhesions and improve overall hand function. It’s important to perform these movements slowly and within a comfortable range to avoid discomfort. Tendon gliding exercises are particularly beneficial for individuals recovering from hand injuries or managing conditions like arthritis. Consistency in performing these exercises can significantly enhance finger dexterity and independence in daily activities.
Opposition Exercises
Opposition exercises focus on improving the ability to bring the thumb and fingers together, a crucial movement for grasping and manipulating objects. A common exercise involves touching the thumb to each fingertip, one at a time, forming an “O” shape. After making contact, the hand is opened wide before repeating the motion. This exercise enhances thumb mobility and coordination, essential for tasks like writing or using utensils. Another variation involves placing the hand flat and lifting each finger one by one to meet the thumb, promoting finger independence and dexterity. These exercises are particularly beneficial for individuals with limited thumb movement or conditions like arthritis. Performing opposition exercises slowly and within a comfortable range helps avoid discomfort while maximizing benefits. Regular practice can improve hand function, making daily activities easier and more manageable.
Pronation and Supination Exercises
Pronation and supination exercises target the forearm and wrist, enhancing the ability to rotate the hand palm-down (pronation) and palm-up (supination). A common exercise involves holding a light weight or small object, such as a hammer, and slowly rotating the forearm to alternate between palm-up and palm-down positions. Another effective exercise is rolling a small bottle or cylinder on a flat surface using the forearm and wrist. These movements improve forearm mobility and wrist flexibility, which are essential for tasks like turning doorknobs or using tools. Patients are often advised to perform these exercises slowly and within a comfortable range to avoid strain. Regular practice can enhance functional abilities, making daily activities requiring forearm rotation easier to perform. These exercises are particularly beneficial for individuals recovering from wrist injuries or managing conditions like arthritis.

Benefits of Occupational Therapy Hand Exercises
Occupational therapy hand exercises improve dexterity, strength, and range of motion, reducing stiffness and pain while enhancing grip strength and coordination for daily activities and independence.
Improving Dexterity and Strength
Occupational therapy hand exercises are designed to enhance dexterity and strength, enabling individuals to perform daily tasks with greater ease. These exercises often involve tools like therapy putty, which provides resistance to strengthen finger and hand muscles. Activities such as squeezing putty, pinching coins, or manipulating small objects improve fine motor skills and coordination. Passive and active motion exercises also play a role in maintaining or restoring hand function, even when active movement is challenging. Consistent practice of these exercises can lead to noticeable improvements in grip strength and overall hand agility, making everyday activities more manageable. Regular engagement in these routines, guided by occupational therapists, ensures a tailored approach to rebuilding dexterity and strength effectively;
Enhancing Range of Motion
Occupational therapy hand exercises focus on improving joint mobility and flexibility, essential for restoring natural hand movement; Exercises like tendon gliding, opposition, and pronation/supination help maintain or increase the range of motion, reducing stiffness. Passive motion exercises, where the uninjured hand assists the injured one, are particularly effective for individuals with limited active movement. These routines promote proper joint alignment and prevent unnecessary swelling. Regular practice enhances flexibility, allowing individuals to perform daily tasks with greater ease. Consistency in these exercises, guided by occupational therapists, ensures progressive improvement in hand function and overall mobility, making everyday activities more manageable and reducing discomfort over time.
Reducing Stiffness and Pain
Occupational therapy hand exercises are designed to alleviate stiffness and pain, particularly for individuals with conditions like arthritis or injuries. Gentle stretching and passive motion exercises help improve joint mobility without causing discomfort. Therapy putty and other tools are used to strengthen muscles while minimizing strain. Exercises like tendon gliding and opposition movements promote smooth joint function, reducing stiffness. It’s important to perform these exercises slowly and within a pain-free range to avoid aggravating the condition. Over time, consistent practice can significantly reduce stiffness and pain, enhancing overall hand function and comfort. Always consult with an occupational therapist to tailor exercises to individual needs and ensure safe, effective progress.
Improving Grip Strength
Improving grip strength is a key focus of occupational therapy hand exercises, essential for daily activities like holding objects or writing. Therapy putty is widely used for this purpose, with exercises such as the power grip, where the putty is squeezed firmly, and the flat pinch, which involves pinching the putty between the fingers. These exercises target the intrinsic muscles of the hand, enhancing overall grip strength. Additionally, using coins or small objects to practice picking up and holding items can further strengthen the grip. Regular practice of these exercises can significantly improve dexterity and the ability to perform tasks requiring a firm grasp. Consistency and proper technique are crucial to achieving optimal results and preventing strain or injury.
Enhancing Coordination and Function
Occupational therapy hand exercises are designed to enhance coordination and function, enabling individuals to perform daily tasks with greater ease and precision. Activities such as picking up coins, buttons, or small objects help improve dexterity and fine motor skills. Using textured items like cotton balls or fabric stimulates sensory awareness, further refining hand-eye coordination. Exercises like touching fingertips to the thumb and opening the hand wide promote functional movement. These routines are particularly beneficial for individuals with conditions such as arthritis or limited mobility. By strengthening hand function and improving coordination, individuals can regain independence in activities like writing, cooking, or dressing. Regular practice, guided by an occupational therapist, ensures progress and adaptability to specific needs, making these exercises a cornerstone of hand rehabilitation programs.

Creating a Hand Exercise Routine
Creating a hand exercise routine involves setting realistic goals, designing a daily plan with specific exercises, and tracking progress to ensure consistent improvement and adaptation.
Setting Goals for Hand Rehabilitation
Setting clear and achievable goals is essential for effective hand rehabilitation. These goals should align with the individual’s daily needs and functional priorities, ensuring exercises are tailored to improve specific skills like dexterity, strength, or range of motion. For instance, a goal might focus on enhancing grip strength to perform tasks such as opening jars or improving finger coordination for activities like writing. Goals should be measurable and time-bound, allowing progress to be tracked and celebrated. Consulting with an occupational therapist ensures goals are realistic and personalized, addressing the individual’s unique challenges. Regularly reviewing and adjusting these goals helps maintain motivation and ensures the rehabilitation process remains focused and effective. By setting clear objectives, individuals can better understand their progress and stay committed to their hand exercise routine.
Designing a Daily Exercise Plan
Creating a structured daily exercise plan is crucial for consistent progress in hand rehabilitation. Begin with warm-up activities, such as gentle finger bends or wrist rotations, to prepare the hands for more intense exercises. Incorporate a variety of exercises, such as therapy putty squeezing, coin picking, and passive motion stretches, to target different aspects of hand function. Allocate specific time slots for each exercise, ensuring a balance between strength, flexibility, and dexterity. For example, dedicate 10 minutes to therapy putty exercises, 5 minutes to coin or button activities, and 5 minutes to passive stretching. Include breaks to avoid fatigue and maintain focus. Consistency is key, so aim to perform exercises at the same time daily. Track progress by noting improvements in range of motion, strength, or task completion speed. Adjust the plan as needed to reflect changes in ability or goals, ensuring continued challenge and growth. Always prioritize comfort and avoid pain during exercises.
Tracking Progress and Adjustments
Monitoring progress in hand exercises is essential to ensure effectiveness and guide adjustments. Keep a journal to record the number of repetitions, duration, and any improvements in strength or dexterity. Note changes in pain levels or ease of performing tasks. Regularly review goals to assess if they are being met or need modification. For example, if finger bending becomes easier, increase resistance using therapy putty or add more complex exercises. Adjustments may involve introducing new challenges, such as smaller objects for picking or more intricate movements. Consult with an occupational therapist to refine the plan based on progress. Celebrate small achievements to stay motivated and maintain consistency. Tracking ensures the exercise plan remains tailored to individual needs, promoting continuous improvement and adaptation. Regular feedback loops help in optimizing the rehabilitation process for better outcomes.
Using Therapy Tools and Resources
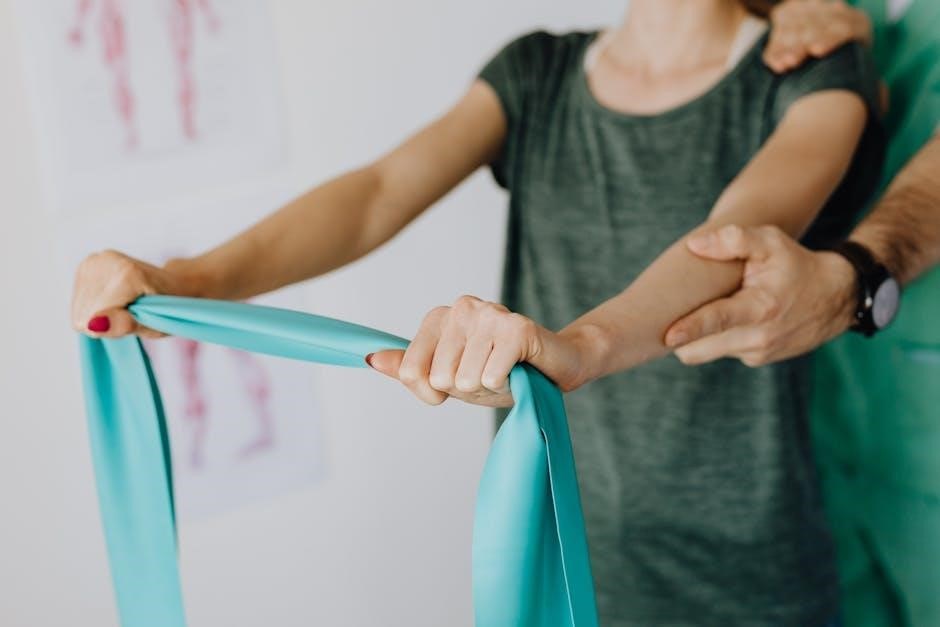

Therapy tools like putty, coins, and textured items enhance hand strength and dexterity. Downloadable PDF guides provide structured exercise routines for effective rehabilitation and independence.
Therapy Putty for Hand Strengthening
Therapy putty is a versatile tool used in occupational therapy to enhance hand strength, dexterity, and finger coordination. It offers varying resistance levels, allowing individuals to progress as their strength improves. Common exercises include the power grip, where the putty is squeezed into a flat shape, and the flat pinch, which involves pinching the putty to maintain a specific shape. These exercises target the intrinsic muscles of the hand, improving grip strength and endurance. Therapy putty is particularly beneficial for individuals recovering from hand injuries or managing conditions like arthritis. It is often recommended to start with lighter resistance and gradually increase as hand function improves. Regular use of therapy putty can lead to noticeable improvements in hand function and overall dexterity.
Coins, Buttons, and Small Objects for Dexterity
Exercises using coins, buttons, and small objects are effective for improving hand dexterity and fine motor skills. These activities involve picking up and manipulating small items, such as coins or buttons, to enhance finger coordination and precision. For example, placing a coin on the back of the hand and flipping it over using the fingers can improve dexterity. Another exercise involves transferring small objects from one container to another, which strengthens grip and finger function. These exercises are particularly beneficial for individuals with conditions like arthritis or those recovering from hand injuries. They are simple, cost-effective, and can be tailored to different skill levels. Regular practice helps improve hand function, making daily tasks easier to perform. Supervision may be necessary to ensure proper technique and safety during these exercises.
Textured Items for Sensory Stimulation
Textured items, such as cotton balls, paint brushes, light sandpaper, and fabrics like satin or Velcro, are used in occupational therapy to enhance sensory awareness and tactile perception. These tools help individuals develop sensitivity in their hands, which is crucial for tasks requiring precision. For example, gently touching different textures can improve finger awareness and coordination. This type of stimulation is particularly beneficial for those with sensory processing challenges or hand injuries. The variety of textures provides a calming and engaging experience, making it easier for individuals to focus on their hand movements. These exercises are often combined with other therapies to promote overall hand function and dexterity. Regular use of textured items can lead to improved sensory integration, aiding in daily activities that require fine motor skills and tactile discrimination.
Downloadable PDF Guides for Hand Exercises
Downloadable PDF guides for hand exercises are valuable resources for individuals seeking to improve hand function and strength. These guides typically include detailed instructions, diagrams, and step-by-step exercises tailored to enhance dexterity, range of motion, and grip strength. Many PDFs are designed for both patients and therapists, offering a structured approach to hand rehabilitation. They often feature exercises like tendon gliding, opposition, and pronation/supination, along with activities using therapy putty or small objects. Some guides also include progress-tracking sheets, allowing users to monitor their improvement over time. These resources are particularly useful for home use, providing a convenient and accessible way to practice hand exercises consistently. By following the exercises outlined in these guides, individuals can work toward regaining independence in daily activities and improving overall hand function.
Safety and Precautions
Always consult a physician or occupational therapist before starting hand exercises. Avoid pain during exercises, focus on discomfort, and ensure proper alignment and technique. Supervision is recommended for safety.
Consulting with a Physician or Occupational Therapist
Consulting with a physician or occupational therapist is crucial before starting hand exercises, especially for individuals with specific conditions like arthritis or injuries. They provide personalized recommendations, ensuring exercises are safe and effective. A therapist can design a tailored plan, monitor progress, and adjust activities as needed. This professional guidance helps avoid overexertion or improper techniques that might worsen conditions. It’s essential to follow their advice to maximize benefits and prevent complications. Regular check-ins ensure the exercises remain appropriate and aligned with recovery goals. Avoiding pain during exercises is emphasized, as discomfort should not lead to injury. Proper alignment and technique are also stressed to maintain safety and effectiveness. Supervision, particularly for those with limited mobility, ensures exercises are performed correctly and safely.
Avoiding Pain During Exercises
Avoiding pain during hand exercises is essential to prevent further injury or discomfort. Exercises should focus on discomfort rather than pain, as pain can indicate overexertion or improper technique. It’s important to stop immediately if pain occurs and consult a healthcare professional. Gentle, controlled movements are recommended to promote healing and strength without causing harm. Pushing through pain can lead to inflammation or prolonged recovery. Instead, aim for gradual progress, allowing hands to adapt to the exercises. Proper alignment and technique, guided by a therapist, can help minimize discomfort. Remember, the goal is to improve function and strength, not to endure pain. Always prioritize safety and comfort to achieve effective and sustainable results.
Proper Alignment and Technique
Proper alignment and technique are crucial for effective and safe hand exercises in occupational therapy. Maintaining correct posture ensures that exercises target the intended muscles without causing strain. For example, exercises should be performed with arms at a right angle and forearms resting on a table to maintain proper alignment. Using tools like therapy putty requires precise grip and movement techniques to avoid injury. Following the guidance of an occupational therapist helps ensure that exercises are performed correctly. Proper technique also involves slow, controlled movements rather than jerky or forced actions. This approach minimizes the risk of overexertion and promotes optimal healing. By focusing on correct form, individuals can maximize the benefits of their hand exercises while maintaining safety and effectiveness.
Supervision for Safe Exercise Practices
Supervision is essential for ensuring safe and effective hand exercises in occupational therapy. A responsible adult or therapist should oversee exercises to guide proper technique and prevent overexertion. This is particularly important for individuals with physical or cognitive challenges. Supervision helps identify potential risks, such as improper alignment or excessive force, which could lead to injury. It also ensures that exercises are performed within a pain-free range, as pain can indicate improper execution or overuse. Direct observation allows for immediate feedback and adjustments, promoting a safe and productive routine. Supervision further helps track progress and adapt exercises as needed. By prioritizing supervision, individuals can maximize the benefits of their hand exercises while minimizing risks and ensuring long-term safety.

Consistent practice of occupational therapy hand exercises empowers individuals to regain independence, enhancing hand function and overall well-being through structured, goal-oriented routines.
The Role of Consistency in Hand Rehabilitation
Consistency is vital in hand rehabilitation, as regular practice strengthens muscles, improves dexterity, and enhances functional abilities. Performing exercises like tendon gliding and opposition exercises daily ensures progressive improvement. Over time, consistent effort reduces stiffness, boosts mobility, and restores coordination. Patience is key, as gradual progress leads to lasting results. Sticking to a structured routine, even when challenging, fosters independence and confidence. Regular practice also prevents setbacks, maintaining gains and promoting long-term recovery. By committing to consistent hand exercises, individuals can achieve meaningful improvements in hand function and overall quality of life.
Occupational Therapy as a Path to Independence
Occupational therapy serves as a powerful pathway to independence by empowering individuals to regain control over daily activities. Through tailored hand exercises and tools like therapy putty, patients rebuild strength, dexterity, and coordination. This structured approach enables individuals to perform tasks with greater ease, fostering confidence and self-reliance. The ultimate goal of occupational therapy is to help individuals achieve independence in their personal and professional lives, ensuring they can engage fully in activities that bring fulfillment and purpose. By addressing physical and functional challenges, occupational therapy creates a foundation for lasting independence and improved quality of life.